In today’s world, banks are an integral part of the global financial system, helping to drive economic growth, foster innovation, and support everyday financial transactions. However, many people may not fully understand what constitutes a bank or the specific functions it serves. To break it down, let’s explore what banks are and examine their primary roles in both individual and institutional economies.
What is a Bank?
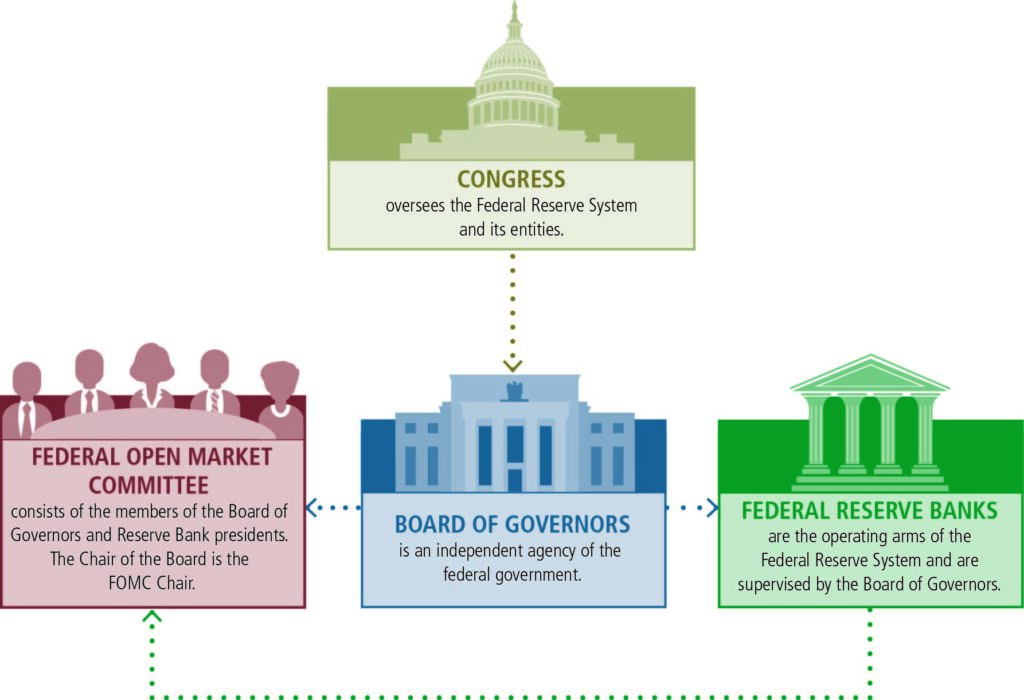
A bank is a financial institution that is authorized to accept deposits from the public, provide loans, and offer various financial services. The primary role of a bank is to act as an intermediary between those who have surplus funds (depositors) and those who need capital (borrowers). Banks are typically regulated by government agencies to ensure they operate in a secure and sound manner, protecting both consumers and the broader economy.
The banking sector is diverse, with institutions ranging from commercial banks and savings banks to investment banks and central banks. Each type of bank serves a different set of financial needs, but they all share a common foundation in managing money and facilitating financial transactions.
Primary Functions of a Bank
Banks perform a variety of functions that contribute to the stability and growth of the economy. Below are the key functions banks fulfill:
1. Accepting Deposits
One of the most basic functions of a bank is to accept deposits from individuals, businesses, and organizations. These deposits can take various forms, including savings accounts, checking accounts, and fixed deposits. By accepting deposits, banks provide a safe place for individuals and businesses to store their money while earning interest, depending on the type of account.
Types of Deposits:
- Demand Deposits: These are funds held in checking accounts that can be withdrawn at any time without any advance notice.
- Time Deposits: These are fixed deposits where the funds are held for a set period, and the account holder earns a higher interest rate in return for committing their funds for a fixed term.
2. Providing Loans and Credit
Banks play a critical role in lending money to individuals, businesses, and governments. By providing loans, banks help stimulate economic activity by enabling borrowers to make significant investments, such as purchasing homes, starting or expanding businesses, or funding infrastructure projects.
Banks offer a range of loan products, including:
- Personal Loans: These are unsecured loans granted to individuals for personal purposes, such as buying a car or paying off debts.
- Business Loans: Banks offer financing options to businesses, allowing them to grow, expand, and maintain operations.
- Mortgages: A type of loan provided to individuals or businesses to purchase real estate.
- Credit Lines: These provide individuals or companies with access to a set amount of credit that can be used as needed.
3. Facilitating Payments
Banks act as intermediaries in facilitating payments for goods and services, both domestically and internationally. They provide various tools to help individuals and businesses conduct transactions, such as:
- Wire Transfers: Electronic transfers of funds between banks, both domestically and across borders.
- Credit and Debit Cards: Payment cards issued by banks that enable users to make purchases and access their funds.
- Online Banking: A platform that allows customers to perform banking transactions, such as transferring funds, paying bills, and checking account balances, from the comfort of their homes.
4. Wealth Management and Investment Services
Banks also offer wealth management and investment services to individuals and businesses. These services typically include investment advice, portfolio management, retirement planning, and financial consulting. Banks may offer a wide variety of investment products such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and insurance products to help clients grow their wealth over time.
For businesses, banks may offer advisory services for mergers and acquisitions, financial planning, and capital raising through public or private offerings. Investment banks, in particular, specialize in these complex financial services.
5. Currency Exchange
Banks facilitate the exchange of one currency for another, playing a key role in both international trade and travel. By offering currency exchange services, banks make it easier for businesses and individuals to conduct cross-border transactions. The exchange rates offered by banks can vary, and they typically charge a small fee or margin for this service.
6. Safekeeping and Custody Services
Banks often offer safe deposit boxes where individuals and businesses can store valuable items such as important documents, jewelry, and financial assets. Furthermore, banks provide custodial services for investment funds, ensuring that assets are protected, monitored, and managed according to legal and regulatory standards.
7. Risk Management and Insurance
Through various financial products, banks help individuals and businesses manage risk. Banks often offer insurance products, including life insurance, health insurance, property insurance, and credit insurance, designed to protect against unforeseen circumstances that could cause financial strain.
Additionally, some banks may provide hedging products, such as derivatives, to help businesses manage risk in currency exchange rates, interest rates, or commodity prices.
8. Monetary Policy and Economic Stability (Central Banks)
Central banks, which are government-owned institutions, play an essential role in the economic stability of a country. Unlike commercial banks, central banks do not focus on generating profits but on regulating and managing the national money supply and maintaining the stability of the financial system.
Central banks perform the following crucial functions:
- Controlling Inflation: By adjusting interest rates and influencing money supply, central banks can help control inflation, stabilizing the currency and the economy.
- Regulating Commercial Banks: Central banks oversee and regulate commercial banks to ensure they follow proper practices, maintain solvency, and protect depositors’ funds.
- Lender of Last Resort: Central banks provide liquidity to commercial banks in times of financial distress, preventing bank failures and maintaining public confidence in the banking system.
Conclusion
Banks are fundamental institutions in modern economies, providing services that facilitate economic activity, promote investment, and support financial stability. Their core functions, from accepting deposits to offering loans, facilitating payments, and providing financial advice, all serve to meet the needs of individuals, businesses, and governments. Whether through offering credit or safeguarding money, banks play a pivotal role in the global financial ecosystem, ensuring that capital flows smoothly, risks are managed, and economic growth is fostered.
Understanding the wide-reaching functions of banks allows individuals and businesses to make more informed decisions about how to manage and grow their financial assets, ultimately contributing to the overall well-being of the economy.